
These vehicles have small generators connected to the internal combustion engine lowering the friction and hence lowering the fuel consumption. The electric motors are only used as generators for regenerative breaking to charge the car battery.
#TYPES OF HYBRID VEHICLES FULL#
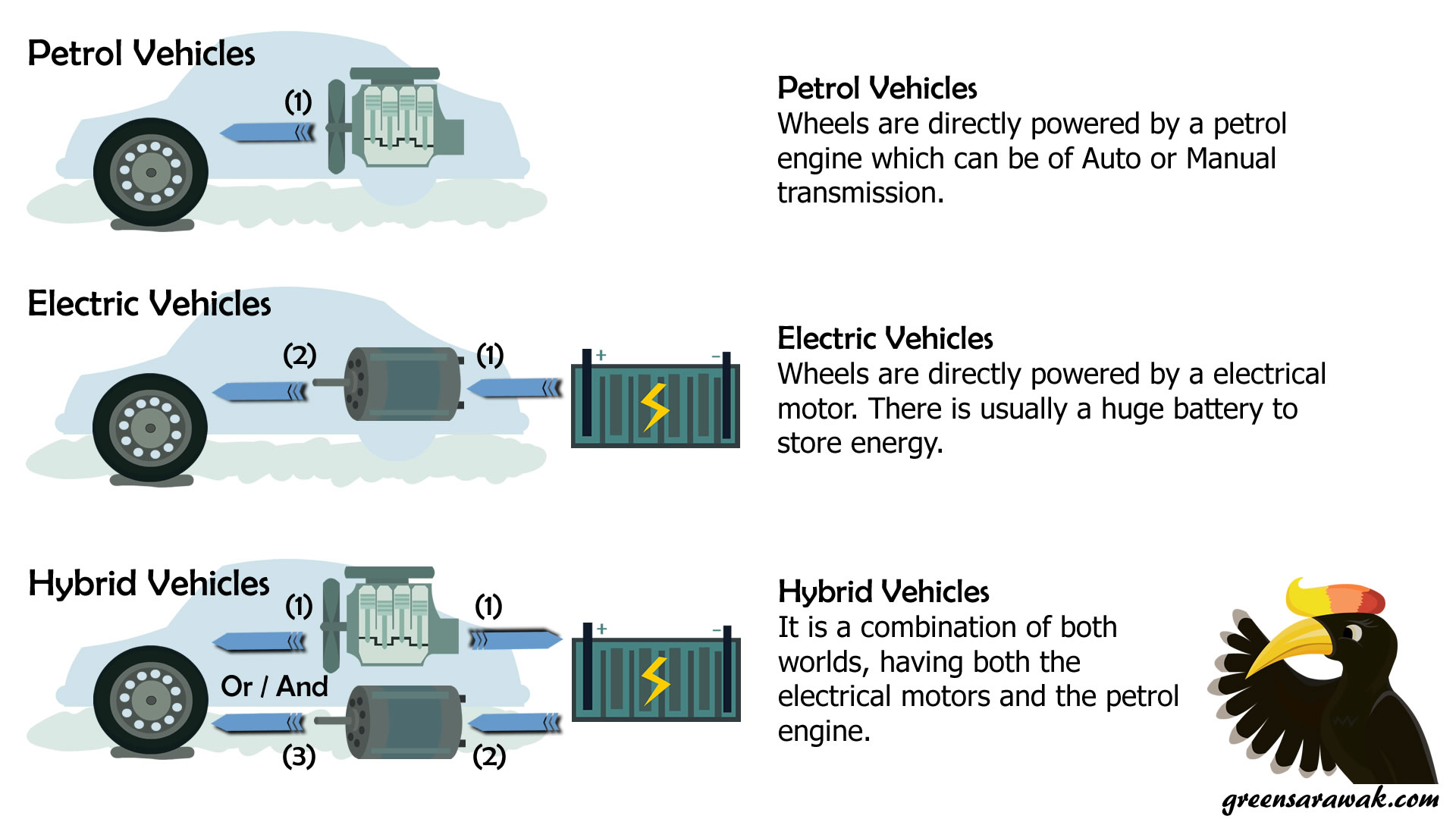
In full hybrid vehicles the electro motors also propel the vehicle at relatively low speeds. However, in hybrid vehicles, electro motors attached to the wheels serve as generators during breaking converting the kinetic energy into electricity.

During breaking the kinetic energy of the vehicle is normally dissipated as heat in the breaking discs. An important technique is regenerative breaking. Hybrids achieve improved efficiencies by employing several techniques. A hybrid car combines an internal combustion engine with technologies used in full electric vehicles. These facts have led to the construction of hybrid vehicles. However, commercialization of full electric vehicles is still hampered by high purchase prices, short driving ranges and long recharging times. The most energy efficient vehicle available today is the electric vehicle. These two technical pathways are complementary. The second technical pathway involves the improvement of the energy efficiency of the vehicles through downsizing of the engine and various levels of hybridization and electrification. The first pathway involves the deployment of low carbon alternative fuels like biofuels, LPG, LNG and CNG. Currently, there are two major technical pathways to GHG emission reductions. They have the advantage of higher fuel efficiency and reduced CO2 emissions without additional infrastructure requirements.Īt present, there is no single good solution to the problem of lowering CO 2 emission in the transport sector. Hybrid vehicles are still more expensive than traditional vehicles using an internal combustion engine. Cars running most of their kilometers on motorways do not benefit from hybridization mostly because on motorways vehicles drive at more or less constant speeds. Small passenger cars benefit the most from strong downsizing in combination with micro hybridization. For passenger cars there are various levels of hybridization possible all giving rise to various amount of CO 2 emission reductions at different costs.
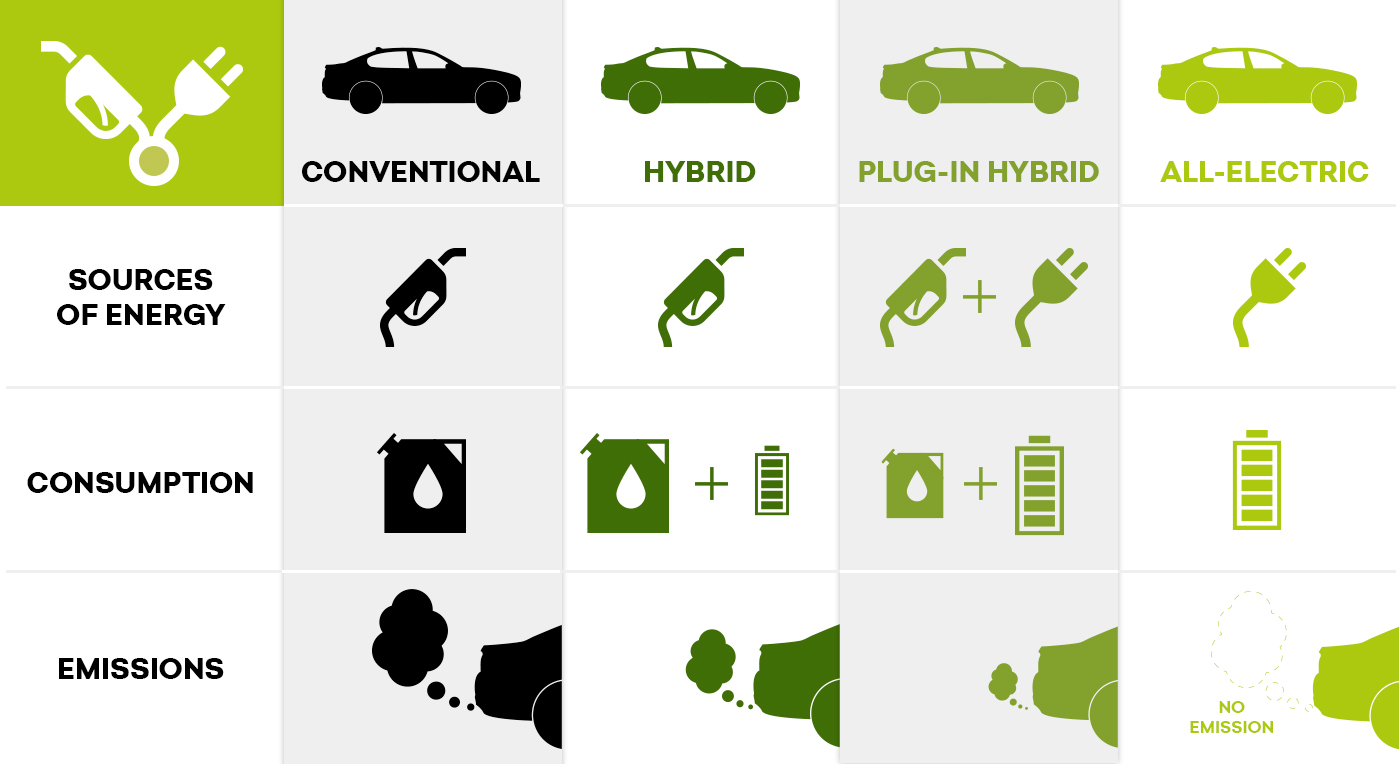
Vehicles employed in urban areas like small passenger cars, local delivery trucks and city busses benefit from hybridization and show substantially lower CO 2 emissions, ranging from 23 to 43% depending on the traffic dynamics. hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors. A hybrid vehicle uses two or more distinct power sources, i.e. One approach to lowering the CO 2 emission from traffic is the hybridization of vehicles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
